Extacting Regions of Interest using Page Markers

Source on GitHub: https://github.com/ayoungprogrammer/OMR-Example
Introduction
Optical Mark Recognition is recognizing certain “marks” on an image and using those marks as a reference point to extract other regions of interest (ROI) on the page. OMR is a relatively new technology and there is close to no documentation on the subject. Current OMR technologies like ScanTron require custom machines designed specifically to scan custom sheets of paper. These methods work well but the cost to produce the machines and paper is high as well as the inflexibility. Hopefully I can provide some insight into creating an efficient and effective OMR algorithm that uses standard household scanners and a simple template.
An OMR algorithm first needs a template page to know where ROI’s are in relation to the markers. It then needs to be able to scan a page and recognize where the markers are. Then using the template, the algorithm can determine where the ROI’s are in relation to the markers. In the case of ScanTrons, the markers are the black lines on the sides and ROI’s are the bubbles that are checked.
For an effective OMR, the markers should be at least halfway across the page from each other (either vertically or horizontally). The further apart the markers are, the higher accuracy you will achieve.
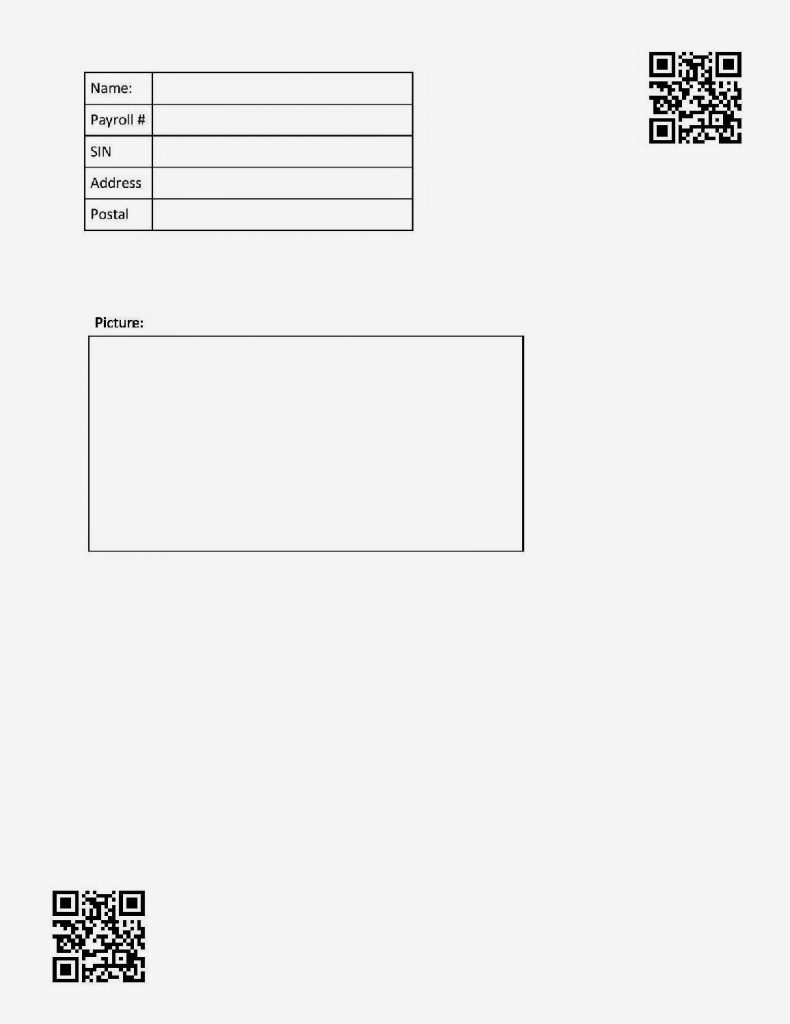
For the simplicity of this tutorial, we will use two QR codes with one in each corner as the markers. This will be our template:
Using the coordinate we can do some simple math to find the relative positioning of the ROI’s.
We can also find the angle of rotation from the markers. If we find the angle between the top right corner and bottom left corner of the template markers we get: 53.48222 degrees. If we find that the markers we scan have is something different from that angle, we rotate the whole page by that angle, it will fix the skewed rotation.
Scanned image:
Extensions
Source Code
Source on Github: https://github.com/ayoungprogrammer/OMR-Example
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include <zbar.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
using namespace zbar;
//g++ main.cpp /usr/local/include/ /usr/local/lib/ -lopencv_highgui.2.4.8 -lopencv_core.2.4.8
void drawQRCodes(Mat img,Image& image){
// extract results
for(Image::SymbolIterator symbol=image.symbol_begin(); symbol != image.symbol_end();++symbol) {
vector<Point> vp;
//draw QR Codes
int n = symbol->get_location_size();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
vp.push_back(Point(symbol->get_location_x(i),symbol->get_location_y(i)));
}
RotatedRect r = minAreaRect(vp);
Point2f pts[4];
r.points(pts);
//Display QR code
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
line(img,pts[i],pts[(i+1)%4],Scalar(255,0,0),3);
}
}
}
Rect makeRect(float x,float y,float x2,float y2){
return Rect(Point2f(x,y),Point2f(x2,y2));
}
Point2f rotPoint(Point2f p,Point2f o,double rad){
Point2f p1 = Point2f(p.x-o.x,p.y-o.y);
return Point2f(p1.x * cos(rad)-p1.y*sin(rad)+o.x,p1.x*sin(rad)+p1.y*cos(rad)+o.y);
}
void drawRects(Mat& img,Point2f rtr,Point2f rbl){
vector<Rect> rects;
Point2f tr(1084,76);
Point2f bl(77,1436);
rects.push_back(makeRect(223,105,603,152));
rects.push_back(makeRect(223,152,603,198));
rects.push_back(makeRect(223,198,603,244));
rects.push_back(makeRect(223,244,603,290));
rects.push_back(makeRect(223,291,603,336));
rects.push_back(makeRect(129,491,765,806));
//Fix rotation angle
double angle = atan2(tr.y-bl.y,tr.x-bl.x);
double realAngle = atan2(rtr.y-rbl.y,rtr.x-rbl.x);
double angleShift = -(angle-realAngle);
//Rotate image
Point2f rc((rtr.x+rbl.x)/2,(rbl.y+rtr.y)/2);
Mat rotMat = getRotationMatrix2D(rc,angleShift/3.14159265359*180.0,1.0);
warpAffine(img,img,rotMat,Size(img.cols,img.rows),INTER_CUBIC,BORDER_TRANSPARENT);
rtr = rotPoint(rtr,rc,-angleShift);
rbl = rotPoint(rbl,rc,-angleShift);
//Calculate ratio between template and real image
double realWidth = rtr.x-rbl.x;
double realHeight = rbl.y-rtr.y;
double width = tr.x-bl.x;
double height = bl.y - tr.y;
double wr = realWidth/width;
double hr = realHeight/height;
circle(img,rbl,3,Scalar(0,255,0),2);
circle(img,rtr,3,Scalar(0,255,0),2);
for(int i=0;i<rects.size();i++){
Rect r = rects[i];
double x1 = (r.x-tr.x)*wr+rtr.x;
double y1 = (r.y-tr.y)*hr+rtr.y;
double x2 = (r.x+r.width-tr.x)*wr +rtr.x;
double y2 = (r.y+r.height-tr.y)*hr + rtr.y;
rectangle(img,Point2f(x1,y1),Point2f(x2,y2),Scalar(0,0,255),3);
//circle(img,Point2f(x1,y1),3,Scalar(0,0,255));
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
Mat img = imread(argv[1]);
ImageScanner scanner;
scanner.set_config(ZBAR_NONE, ZBAR_CFG_ENABLE, 1);
namedWindow("OMR",CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE); //create a window
Mat grey;
cvtColor(img,grey,CV_BGR2GRAY);
int width = img.cols;
int height = img.rows;
uchar *raw = (uchar *)grey.data;
// wrap image data
Image image(width, height, "Y800", raw, width * height);
// scan the image for barcodes
scanner.scan(image);
//Top right point
Point2f tr(0,0);
Point2f bl(0,0);
// extract results
for(Image::SymbolIterator symbol = image.symbol_begin(); symbol != image.symbol_end();++symbol) {
vector<Point> vp;
//Find TR point
if(tr.y==0||tr.y>symbol->get_location_y(3)){
tr = Point(symbol->get_location_x(3),symbol->get_location_y(3));
}
//Find BL point
if(bl.y==0||bl.y<symbol->get_location_y(1)){
bl = Point(symbol->get_location_x(1),symbol->get_location_y(1));
}
}
drawQRCodes(img,image);
drawRects(img,tr,bl);
imwrite("omr.jpg", img);
return 0;
}